How to Find the Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration Given the Position

1. v = v 0 + a t. 2. Δ x = ( v + v 0 2) t. 3. Δ x = v 0 t + 1 2 a t 2. 4. v 2 = v 0 2 + 2 a Δ x. Since the kinematic formulas are only accurate if the acceleration is constant during the time interval considered, we have to be careful to not use them when the acceleration is changing. Also, the kinematic formulas assume all variables are.
4 Easy Ways to Find Velocity (with Pictures) wikiHow

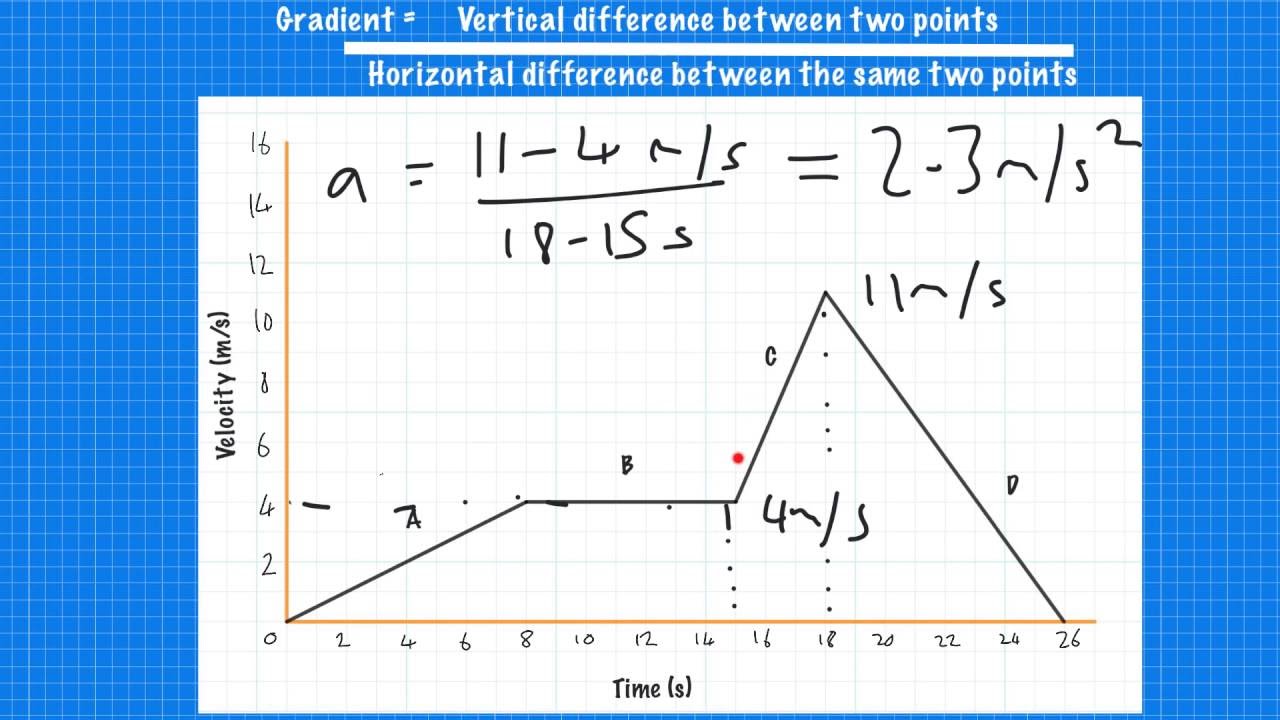
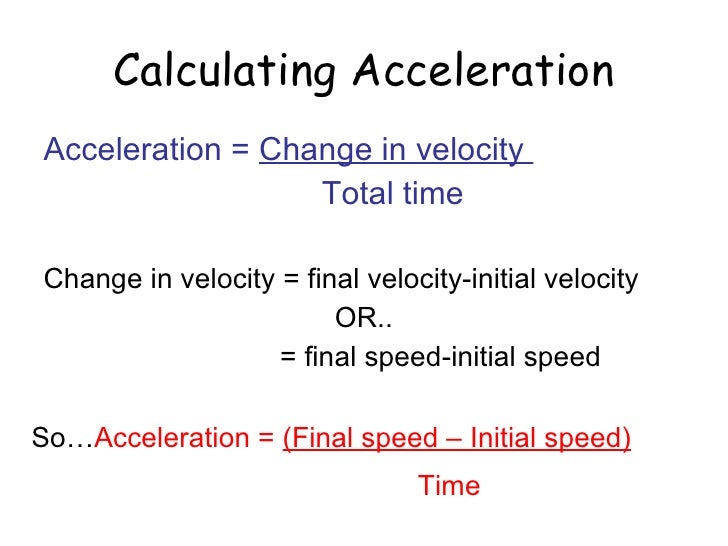
Average Acceleration. Average acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes: a¯ = Δv Δt = vf −v0 tf −t0, (3.4.1) (3.4.1) a ¯ = Δ v Δ t = v f − v 0 t f − t 0, where a¯ a ¯ is average acceleration, v is velocity, and t is time. (The bar over the a means average acceleration.) Because acceleration is velocity in meters divided.
SP1d Velocity/Time Graphs Part 1 Calculating Acceleration YouTube
Acceleration (a) is the change in velocity (Δv) over the change in time (Δt), represented by the equation a = Δv/Δt. This allows you to measure how fast velocity changes in meters per second squared (m/s^2). Acceleration is also a vector quantity, so it includes both magnitude and direction. Created by Sal Khan.
3 Ways to Calculate Acceleration wikiHow

Answer: s = 0 + 1/2 × 9.8 × 4 = 19.6 m/s 2. Therefore, s = 19.6 m/s 2. Acceleration is the change in velocity per time. Acceleration formula can be expressed in terms of initial velocity, final velocity, time taken or distance travelled. Solved examples are useful in understanding the formula.
Speed,velocity,acceleration
In a physics equation, given a constant acceleration and the change in velocity of an object, you can figure out both the time involved and the distance traveled.For instance, imagine you're a drag racer. Your acceleration is 26.6 meters per second 2, and your final speed is 146.3 meters per second.Now find the total distance traveled.
lesson 17 acceleration from velocity time graph YouTube
So a velocity might be "20 m/s, downward". The speed is 20 m/s, and the direction is "downward". Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. Usually, acceleration means the speed is changing, but not always. When an object moves in a circular path at a constant speed, it is still accelerating, because the direction of its velocity is changing.
How to get information about velocity and acceleration from position

Acceleration is the rate of change of an object's speed; in other words, it's how fast velocity changes. According to Newton's second law, acceleration is directly proportional to the summation of all forces that act on an object and inversely proportional to its mass.It's all common sense - if several different forces are pushing an object, you need to work out what they add up to (they may.
What is Velocity? Definition, SI Unit, Examples & Applications The
The right formula to use for calculating velocity depends on a few different factors, such as whether the object is accelerating at a constant rate, or whether it is moving in a circle as opposed to a line.. (initial velocity) + a(t) (acceleration x time). For example, if an object accelerated north at a rate of 5m/s2 over 5 seconds and had.
Acceleration Formula with Velocity and Time YouTube
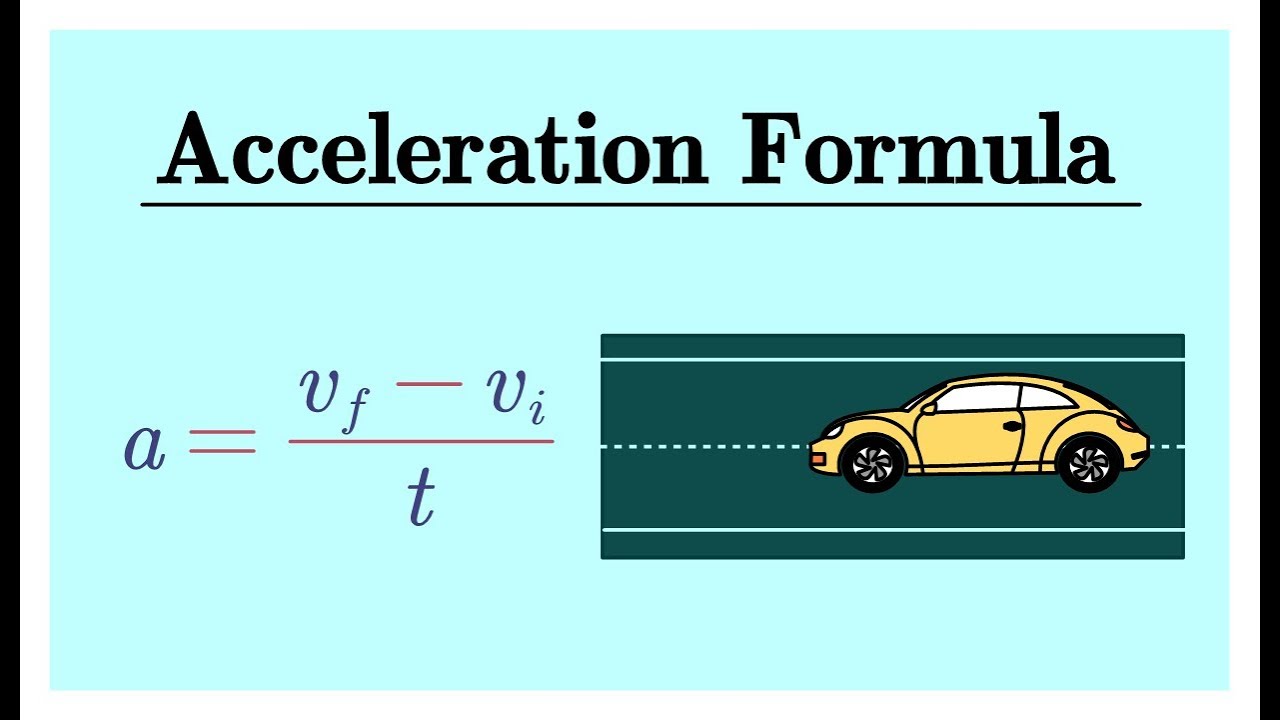
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): (a) Velocity of the motorboat as a function of time. The motorboat decreases its velocity to zero in 6.3 s. At times greater than this, velocity becomes negative—meaning, the boat is reversing direction. (b) Position of the motorboat as a function of time. At t = 6.3 s, the velocity is zero and the boat has stopped.
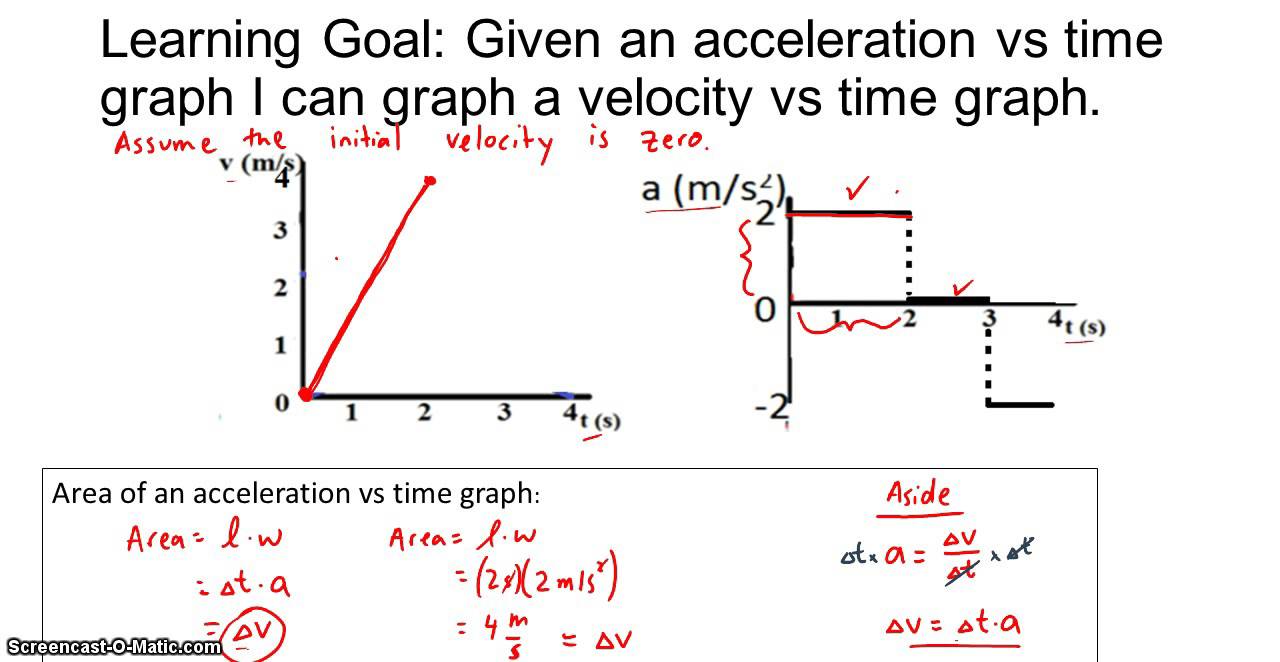
Drawing Velocity Graphs Given Acceleration Graphs YouTube
Velocity Equation in these calculations: Final velocity (v) of an object equals initial velocity (u) of that object plus acceleration (a) of the object times the elapsed time (t) from u to v. v = u + at v = u + a t. Where: u = initial velocity. v = final velocity. a = acceleration. t = time.
How To Calculate Acceleration Velocity And Time Haiper

3. Use the formula to find acceleration. First write down your equation and all of the given variables. The equation is a = Δv / Δt = (vf - vi)/ (tf - ti). Subtract the initial velocity from the final velocity, then divide the result by the time interval. The final result is your average acceleration over that time.
Ex Determine the Velocity Function and Acceleration Function from the

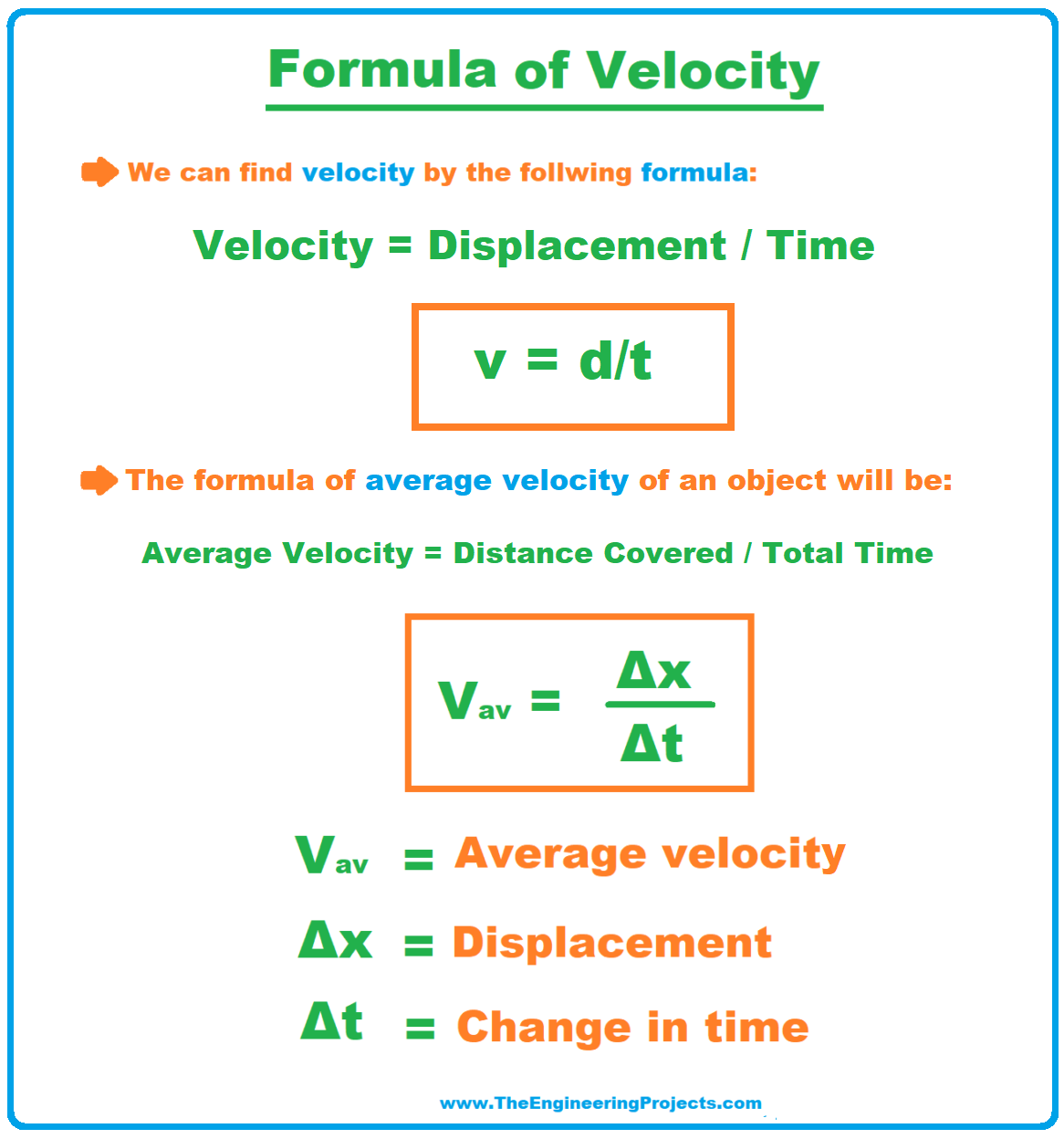
Provided an object traveled 500 meters in 3 minutes, to calculate the average velocity, you should take the following steps: Change minutes into seconds (so that the final result would be in meters per second): 3 minutes = 3 × 60 = 180 seconds. Divide the distance by time: velocity = 500 / 180 = 2.78 m/s.
What is Velocity time graph? physicscatalyst's Blog
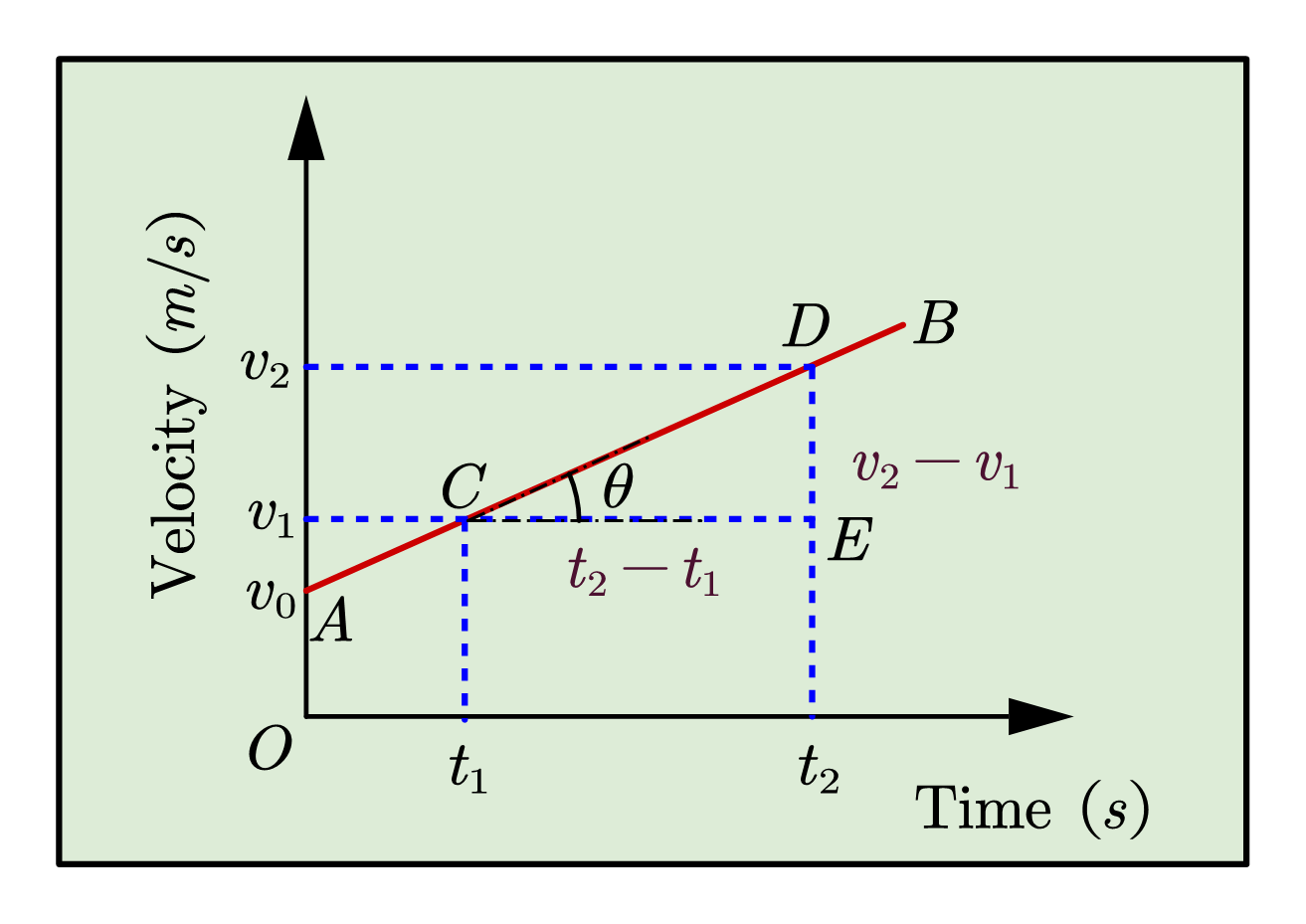
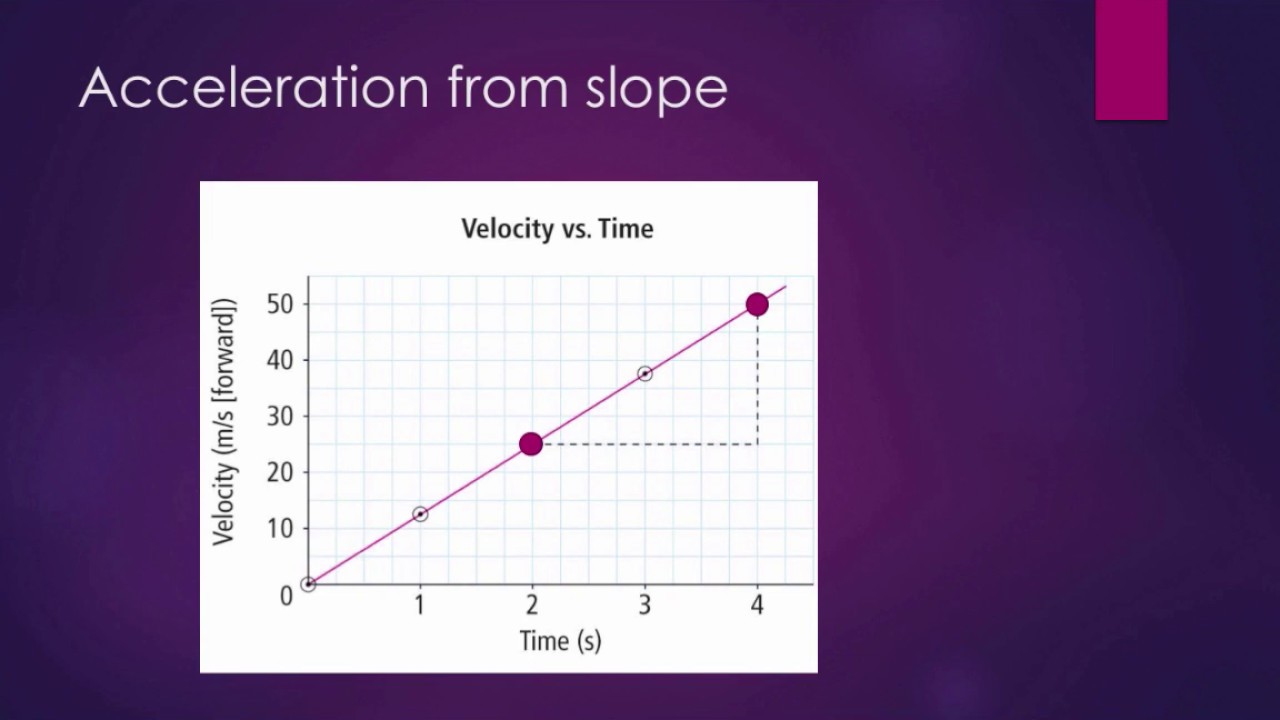
Subtract initial velocity from the final velocity: Δv = v2 - v1. Step 3: Determine Time Interval (Δt) Record the time taken for this change in velocity to occur, usually measured in seconds. Step 4:Calculate Acceleration (a) Apply the formula: Acceleration (a) = Δv / Δt. 4.
Find position or velocity when given acceleration as a function of time

You can use the acceleration equation to calculate acceleration. Here is the most common acceleration formula: a =. Δ v. Δ t. where Δ v is the change in velocity and Δ t is the change in time. You can also write the acceleration equation like this: a =. v ( f) − v ( i)
How to find acceleration on a velocity time graph 1. Velocity and
Figure 3.30 (a) Velocity of the motorboat as a function of time. The motorboat decreases its velocity to zero in 6.3 s. At times greater than this, velocity becomes negative—meaning, the boat is reversing direction. (b) Position of the motorboat as a function of time. At t = 6.3 s, the velocity is zero and the boat has stopped. At times.
Acceleration Formula Physics With Velocity And Time

Calculating Final Velocity Calculate the final velocity of the dragster in Example 3.8 without using information about time. Strategy The equation v 2 = v 0 2 + 2 a (x − x 0) v 2 = v 0 2 + 2 a (x − x 0) is ideally suited to this task because it relates velocities, acceleration, and displacement, and no time information is required. Solution